Hepatitis B is a virus that infects the liver and increases risk of liver failure, liver cancer, or scarring of the liver.
How is Hepatitis B spread?
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood or bodily fluids of an infected individual.1
Symptoms
Symptoms1 of hepatitis B can range from being mild to severe, and usually appear about 1 to 4 months after infection. Oftentimes, infected individuals will appear asymptomatic.

Fever
Weakness and Fatigue

Joint Pain

Abdominal Pain

Dark Urine

Vomiting
Acute and Chronic Hepatitis B2
Acute Hepatitis B infection: lasts less than 6 months. This will likely be cleared from the immune system and complete recovery should occur within a few months.
Chronic Hepatitis B infection: lasts 6 months or longer. At this point, your immune system cannot fight off the virus. Having a chronic infection can lead to serious complications.
Complications
Chronic Hepatitis B can lead to serious complications2, which include:
Liver Cancer
Liver Failure
Cirrhosis of the liver (scarring of liver tissue)
Hepatitis B Vaccine Safety
The Hepatitis B vaccine does not contain any live viruses, and thus cannot cause the disease. Common side effects that are associated with this vaccine (i.e. redness at injection site, mild fever, joint pain) can expected as with most medications.
Hepatitis B Vaccine Effectiveness
Figure 1.3
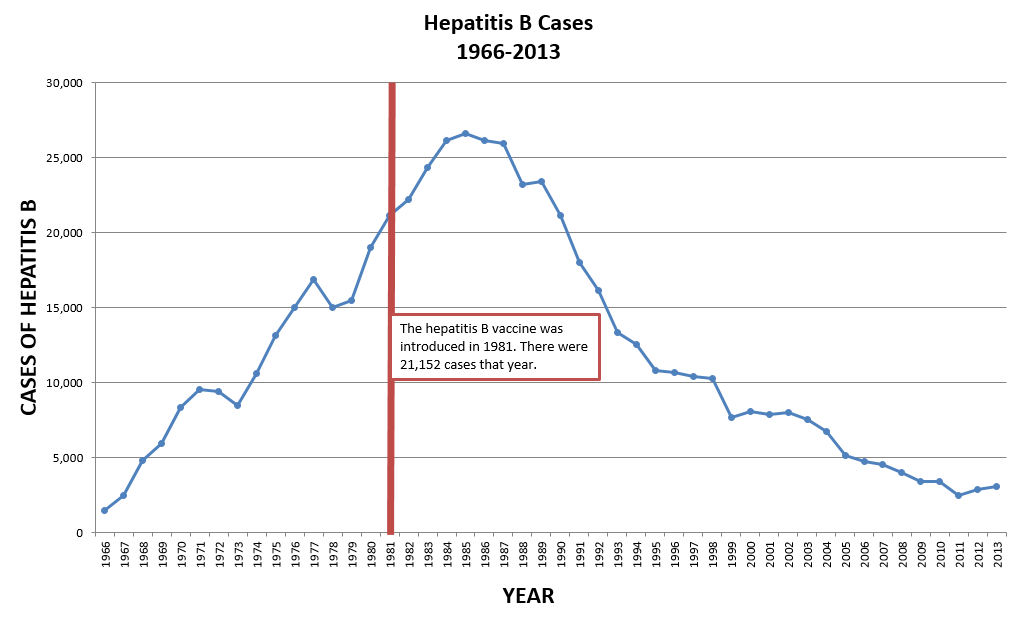
This graph shows reported cases of Hepatitis B in the United States from 1966 to 2013. Notice how there is an overall decline of reported cases since the implementation of the vaccine in 1981.
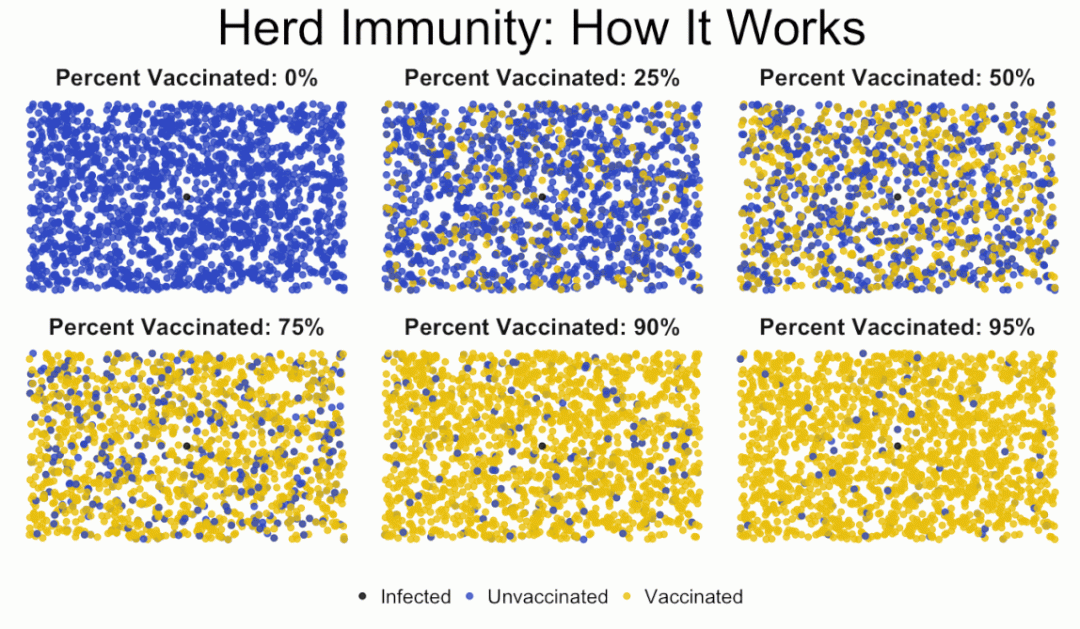
Communities that have very high rates of vaccination further benefit from herd immunity, conferring increased protection to those unable to receive the vaccination.
Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
Present Vaccine schedule based on CDC recommendations4 for the Hepatitis B vaccine. Click here for more information regarding the vaccination schedule.
How do I know if I am protected against Hepatitis B?
Your vaccination records are the best way of knowing if you have been vaccinated. If these records cannot be found, your doctor may perform a blood test. Speak with your doctor if you are unsure about your immune status.
Name: Engerix-B
Manufacturer: GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals
Protections Conferred: Hepatitis B
Age Range: administered shortly after birth
Vaccine Safety Insert
Name: Recombivax HB
Manufacturer: Merck
Protections Conferred: Hepatitis B
Age Range: administered shortly after birth
Vaccine Safety Insert
Name: Hepsilav
Manufacturer: Dynavax
Protections Conferred: Hepatitis B
Age Range: 18+ yo
Vaccine Safety Insert
Name: Pediarix
Manufacturer: GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals
Protections Conferred: Diptheria, Hepatitis B, Tetanus, Pertussis, Polio
Age Range: administered shortly after birth
Vaccine Safety Insert
Name: Twinrix
Manufacturer: GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals
Protections Conferred: Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B
Age Range: 18+ yo
Vaccine Safety Insert
Injection site tenderness or soreness

Fever

Injection site rash
Severe Allergic Reactions
In very rare cases, severe allergic reactions have been observed. Let your doctor know if you have ever experienced any allergic reactions to vaccines.
Anaphylaxis has recorded in roughly 1 out of every 1.1 million doses administered.
The Bottom Line
Chronic Hepatitis B is known to be a "silent killer" because those infected often show no symptoms, and early screening tests can show normal results. By the time symptoms do appear, finding an effective treatment is unlikely. Therefore, it is important for children and adults to be vaccinated against this disease so as to decrease the risk of having liver complications.
Sources
1. Vaccine Information Statement. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/vis/vis-statements/hep-b.html. Published April 5, 2019. Accessed May 4, 2020.
2. Hepatitis B. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hepatitis-b/symptoms-cau…. Published October 27, 2017. Accessed May 4, 2020.
3. Hepatitis B - Vaccines - ProCon.org. Vaccines. https://vaccines.procon.org/vaccine-histories-and-impact/hepatitis-b/. Accessed May 4, 2020.
4. Birth-18 Years Immunization Schedule. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/imz/child-adolescent.html?CD…. Published February 3, 2020. Accessed May 4, 2020.