Herd immunity occurs when a higher proportion of a population is immune to a disease.
Some individuals, such as those who are very young or immunocompromised, cannot be vaccinated. High vaccination rates can protect these individuals from becoming infected with these diseases.
How does herd immunity look?
Suppose two hypothetical cities, City A and City B. City A has very low vaccination rates while City B has very high vaccination rates.
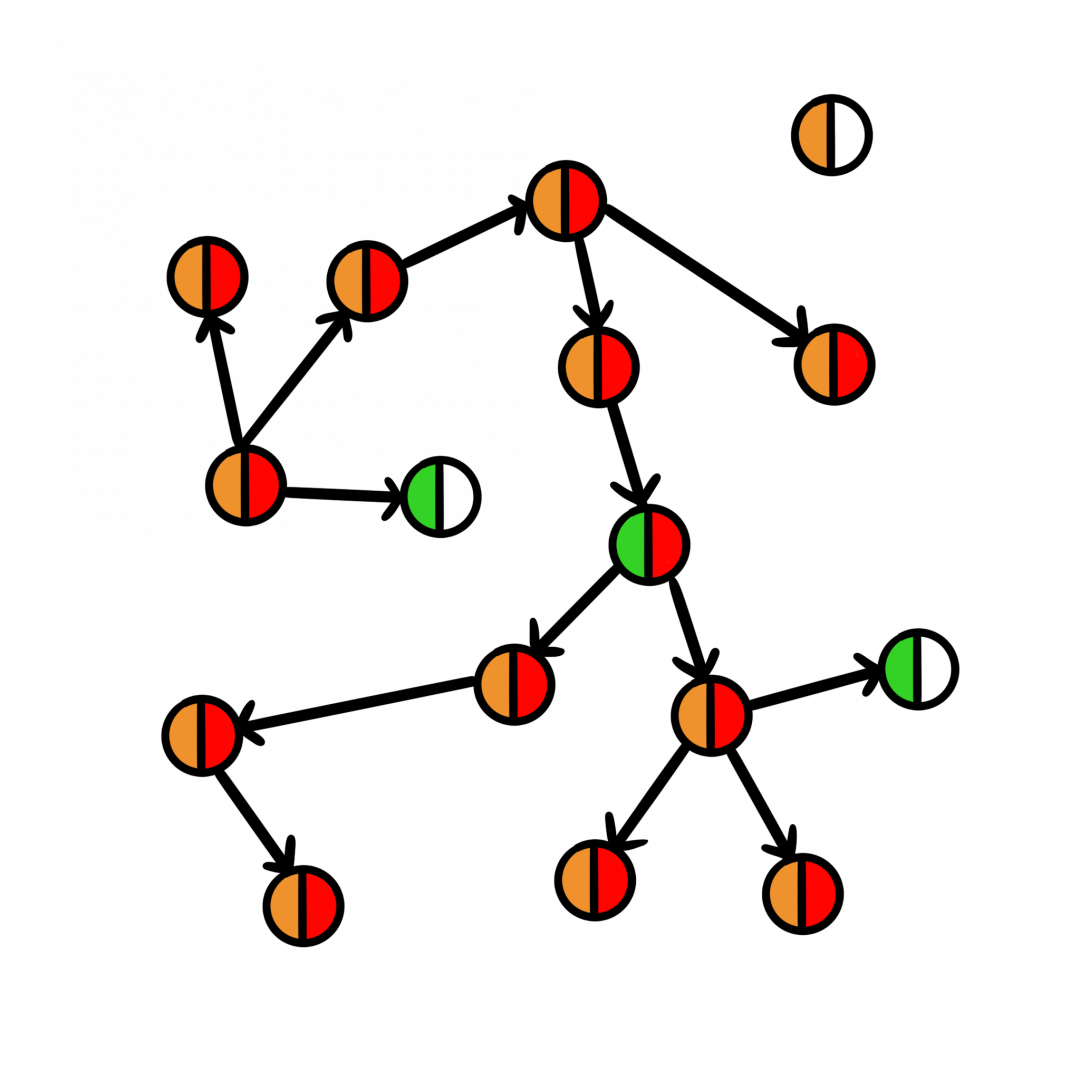
City A
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
In City A, a disease can spread nearly unhindered because most people that the sick individuals interact can become infected and spread the disease. In rare cases, vaccinated individuals can become infected with the disease as well.
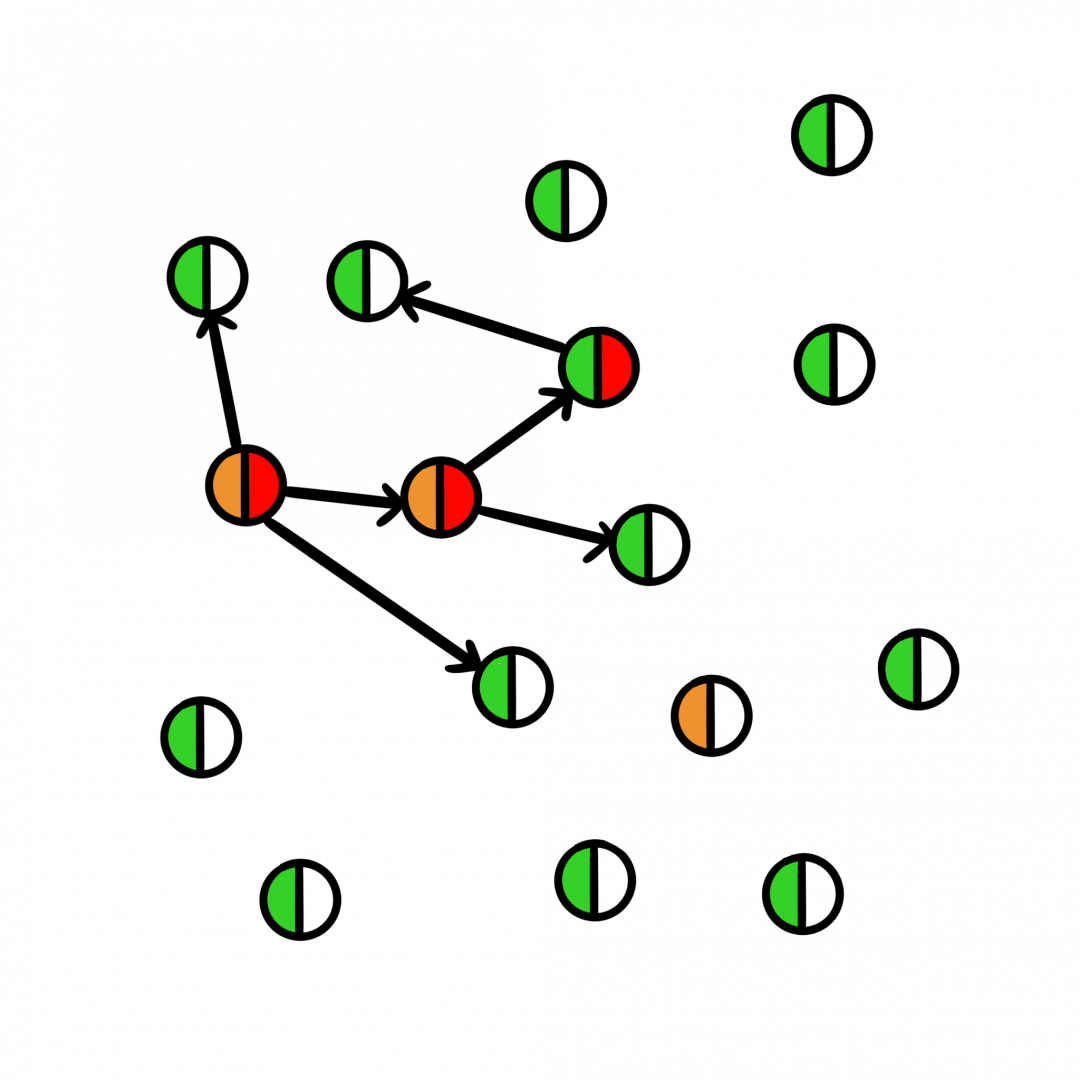
City B
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
In City B, the disease cannot spread very far. While individuals who are not vaccinated may still be at risk for becoming infected and can spread the disease. In some rare cases, vaccines may fail as well. However, high vaccination rates can prevent individuals from becoming sick and protect other community members as well.
Source
1. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Vaccines Protect Your Community. https://www.vaccines.gov/basics/work/protection. Published 2020. Accessed April 20, 2020.
