How is Hepatitis A spread?1

Hepatitis A is spread through fecal-oral routes. Contact with viral particles found in fecal matter (poo) may cause an infection. Basic hand washing hygiene and sanitation of surfaces are especially important in preventing the spread of Hepatitis A.
Poor sanitation may allow the virus causing Hepatitis A to deposit on surfaces or fomites, resulting in further spread.
Symptoms2
Symptoms of hepatitis A are more likely to appear in individuals older than 6. Generally, symptoms last at most 2 months. Symptoms generally begin after 28 days, but range from 15 to 50 days.3

Fever

Fatigue
Loss of Appetite
Nausea

Vomiting

Abdominal Pain

Dark Urine
Diarrhea

Clay-colored stool

Joint pain
Jaundice, or yellowing of the skin/eyes
Complications3
While hepatitis A does not normally cause long-lasting liver damage, in very rare cases it may cause:
Acute liver failure

Death
- Top
- How is it spread?
- Symptoms
- Complications
- Vaccines
Hepatitis A Vaccines

Hepatitis A can be prevented through vaccination.
Hepatitis A Vaccine Safety
Hepatitis A vaccines are killed viruses and are not capable of causing Hepatitis A. Various reviews evaluating the safety of the vaccine support the safety of the vaccine.4-6
Vaccine Effectiveness2
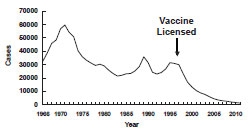
Effective sanitation methods and stronger vaccine recommendations have greatly decreased the number of cases of Hepatitis A per year.
High vaccination rates confer additional protection in the form of herd immunity, such that people who are unable to get vaccinated due to compromised immune system, age, or allergy, may be protected from Hepatitis A.
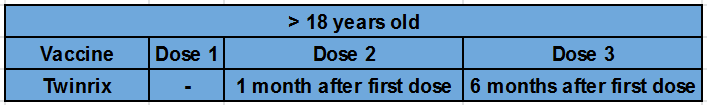
Vaccine Schedules7
How do I know if I am protected against Hepatitis A?
Immunization records are the best way to know if you are vaccinated. Your doctor may perform a blood test to see if you are properly protected; however, you should always speak with your doctor if you have concerns over vaccination.
Types of Hepatitis A Vaccines
Currently, 3 vaccines used in the U.S. to protect against Hepatitis A. Twinrix can also protect individuals from Hepatitis B.
Name: HAVRIX
Manufacturer: GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals
Protections Conferred: Hepatitis A
Age Range: >1 years old
Vaccine Safety Insert

Name: VAQTA
Manufacturer: Merck & Co, Inc
Protections Conferred: Hepatitis A
Age Range: >1 years old
Vaccine Safety Insert
Name: Twinrix
Manufacturer: GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals
Protections Conferred: Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B
Age Range: >18 years old
Vaccine Safety Insert
Side Effects8
Sometimes, the Hepatitis A vaccine may cause some side effects, including:

Injection site soreness/redness

Fever
Headaches

Tiredness

Loss of Appetite
Severe Allergic Reactions
In very rare cases, severe allergic reactions have been observed. Let your doctor know if you have ever experienced any previous allergic reactions to vaccines.
The Bottom Line
Hepatitis A is a highly contagious disease that has acute yet debilitating symptoms. Vaccinations are an effective way of you and those around you from Hepatitis A
Sources
1. Hepatitis A Questions and Answers for the Public. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hav/afaq.htm#C1. Published 2019.
2. Hepatitis A. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Pink Book. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/hepa.html. Published 2019. Accessed May 8, 2020.
3. Hepatitis A. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hepatitis-a/symptoms-cau…. Published 2019. Accessed May 8, 2020.
4. Black S, Shinefield H, Hansen J, Lewis E, Su L, Coplan P. A post-licensure evaluation of the safety of inactivated hepatitis A vaccine (VAQTA®, Merck) in children and adults. Vaccine. 2004;22(5-6):766-772. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2003.08.034
5. Niu MT, Salive M, Krueger C, Ellenberg SS. Two‐Year Review of Hepatitis A Vaccine Safety: Data from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26(6):1475-1476. doi:10.1086/517673
6. Committee to Review Adverse Effects of Vaccines; Institute of Medicine; Stratton K, Ford A, Rusch E, et al., editors. Adverse Effects of Vaccines: Evidence and Causality. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2011 Aug 25. 7, Hepatitis A Vaccine. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK190032/
7. Hepatitis A. US Department of Human & Health Services. https://www.vaccines.gov/diseases/hepatitis_a. Published 2020. Accessed May 9, 2020.
8. Hepatitis A Vaccines: Safety Information. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccinesafety/vaccines/hepatitis-a-vaccine.html. Published 2020. Accessed May 9, 2020.